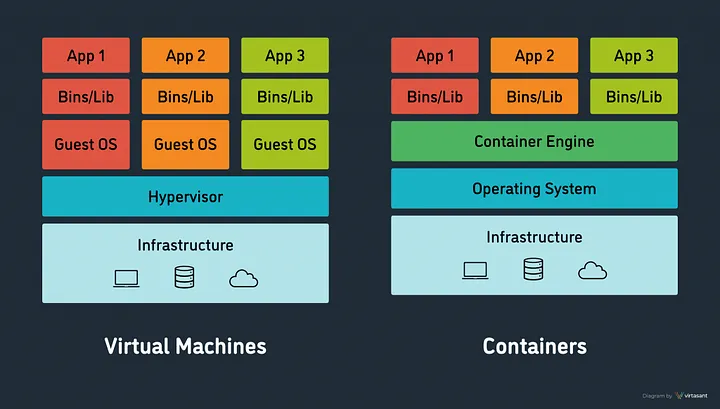
Docker containerization technology is currently trending. Containers are lightweight, and dynamic resource allocation is possible. In contrast, virtual machines, due to their separate operating systems, are heavier and take longer to boot.
Why do we use Docker, and how is it beneficial compared to virtual machines?
Before Docker, the concept of virtual machines was widely used. However, what are the main disadvantages of using virtual machines?
Firstly, each virtual machine has a separate operating system, which results in longer boot times.
Secondly, dynamic resource allocation capabilities are limited.
On the other hand, Docker containers leverage the host operating system for each container, making them lightweight and faster than virtual machines.
Additionally, Docker allows for dynamic resource allocation. Resources can be increased or decreased during runtime.
Let’s understand this with a simple example. Suppose you have purchased a high-configured computer or laptop with an i7 processor, 16 GB RAM, and 1 TB hard disk for 75k. However, you only utilize about 50% of its resources. In such a case, why waste 75k? Depending on your use case, a lower-configured laptop with an i5 processor, 8 GB RAM, and 512 GB hard disk may suffice.
What does this mean?
Simply put, by using Docker containers, we can utilize resources more efficiently.
Does that not make sense?
Mention in the comment box.